Trusted Platform Module (TPM): It is a hardware-based security feature that provides a secure foundation for various security functions on a computer system. It is a microchip that is typically integrated into modern computer systems, including laptops, desktops, servers, and other devices. TPM is a hardware-based security module designed to enhance system security, protect data, ensure platform integrity, and support secure boot processes. Windows incorporated Trusted Platform Module technology starting with Windows Vista, however, with the release of Windows 11, Microsoft made TPM (Trusted Platform Module) 2.0 support mandatory for system compatibility. This means that for a computer to be eligible to install and run Windows 11, it must have a TPM 2.0 chip enabled in the system’s firmware. In this article, we will find out how to check for TPM version in Windows 11.
The following are the steps.
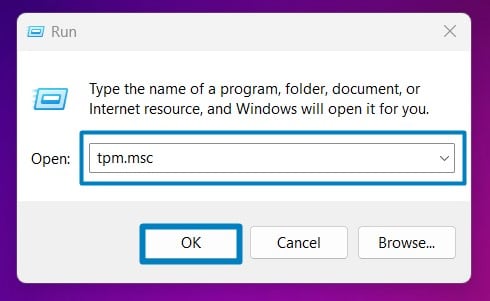
- Open the Run command box using Win Key + R.
- Enter the following command and click OK.
tpm.msc
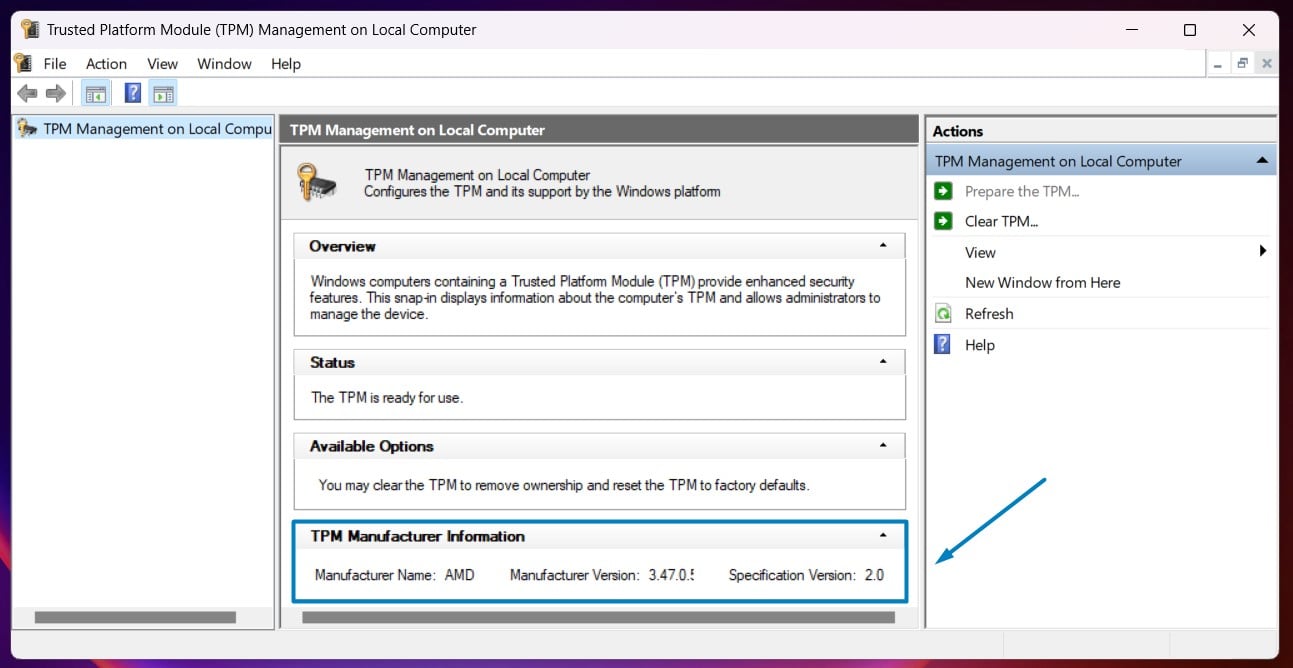
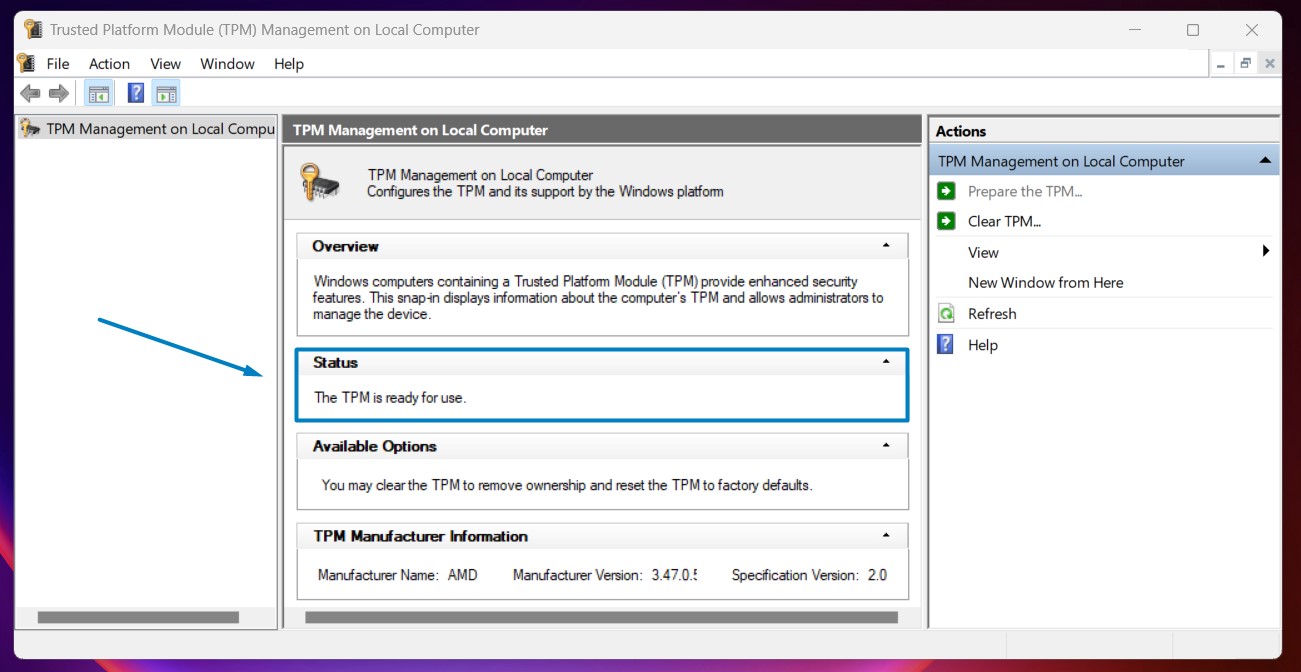
Windows has been incorporating support for TPM technology since Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, and Windows 11 with each subsequent version enhancing and promoting TPM usage for improved security and system integrity features.
Enhanced Security with Trusted Platform Module Firmware:
TPM was introduced in the early 2000s as a collaborative effort between industry leaders, including Intel, Microsoft, IBM, and others. The Trusted Computing Group (TCG) developed and standardized TPM specifications to promote a more secure computing environment.
The first version of TPM, TPM 1.1, was introduced in 2003. Subsequent versions, such as TPM 1.2 and TPM 2.0, introduced improvements, enhanced security features, and expanded functionalities to address evolving security challenges. The latest version TPM 2.0 offers enhanced security features, improved cryptographic capabilities, and better integration with modern hardware and software platforms compared to earlier versions like TPM 1.2.
Purpose of Trusted Platform Module in Computer Systems:

- Security: TPM enhances system security by providing a secure environment for cryptographic operations, such as key generation, encryption, and digital signatures. It helps protect sensitive data, such as encryption keys, passwords, and credentials, from unauthorized access or tampering.
- Platform Integrity: It ensures platform integrity by verifying the boot process and detecting unauthorized changes to critical system components. It can help detect and prevent firmware-level attacks, rootkits, and other forms of malware.
- Secure Boot: It also facilitates secure boot processes by verifying the integrity of the bootloader, operating system, and key system files during startup, thereby ensuring that the system boots from trusted and unaltered components.
- Data Protection: It can encrypt sensitive data stored on the system, providing an additional layer of protection against data breaches and unauthorized access.
Difference between TPM Specification Version & TPM Management Version:
Take away:
It is crucial to verify your system’s TPM version to ensure compatibility with Windows 11’s advanced security features. By following the simple steps outlined in this guide, you can quickly check for TPM version in Windows 11 and take the necessary steps to meet Windows 11 requirements, enhancing your system’s security and performance. Happy Coding! Peace out!
 What is DirectX Shader Cache on Windows 11 OS?
What is DirectX Shader Cache on Windows 11 OS? Install Braille Display with Narrator on Windows 11
Install Braille Display with Narrator on Windows 11 How to Change Mouse Pointer Style on Windows 11?
How to Change Mouse Pointer Style on Windows 11? Quick way to Enable Internet Printing Client on Windows 11
Quick way to Enable Internet Printing Client on Windows 11