The Command Prompt is one of the most essential and powerful utilities available in the Windows operating system. It acts as a back-end tool, allowing users to interact with the system and execute tasks with full potential. From viewing your Wi-Fi password to checking the number of users on your PC, restarting, or shutting down the system, Command Prompt can handle it all!
But for some tasks, the command prompt should have a elevated permission, if you are not using it from the administrator login. You might need to run the command prompt as administrator for performing peculiar tasks! And it is always recommended to use the command prompt with elevated permission because it might help you to executing commands and performing task without any hassle. In this article, I’ve shared the multiple methods to elevate and run command prompt as administrator in Windows 11 pc.
Difference B/W Normal Rights and Admin Rights Command Prompt:
| Feature | Normal Command Prompt | Command Prompt (Run as Administrator) |
|---|---|---|
| Permission Level | Runs with standard user permissions. Limited access to system-level commands and settings. | Runs with elevated permissions. Allows access to system-level commands and configurations. |
| Access to System Files | Restricted. Cannot modify or access critical system files and directories. | Unrestricted. Grants full access to modify and manage system files and directories. |
| Executing Administrative Commands | Not allowed to execute commands that require administrative rights, such as managing disk partitions or enabling/disabling services. | Allows execution of administrative commands, including those for system configurations and troubleshooting. |
| Security | Safer for regular use, as it limits access to critical operations, reducing the risk of accidental changes. | Powerful but risky if misused. Any commands run with elevated permissions can significantly alter the system. |
| Usage Scenarios | Suitable for basic tasks like navigating files, viewing folder contents, and executing non-administrative commands. | Required for advanced tasks like configuring network settings, managing users, or fixing system errors. |
Method 1: Run Command Prompt as Admin using Start Menu:
- Firstly, you need to click the Start icon.
- Now, you need to enter the term “Command Prompt” or “CMD“.
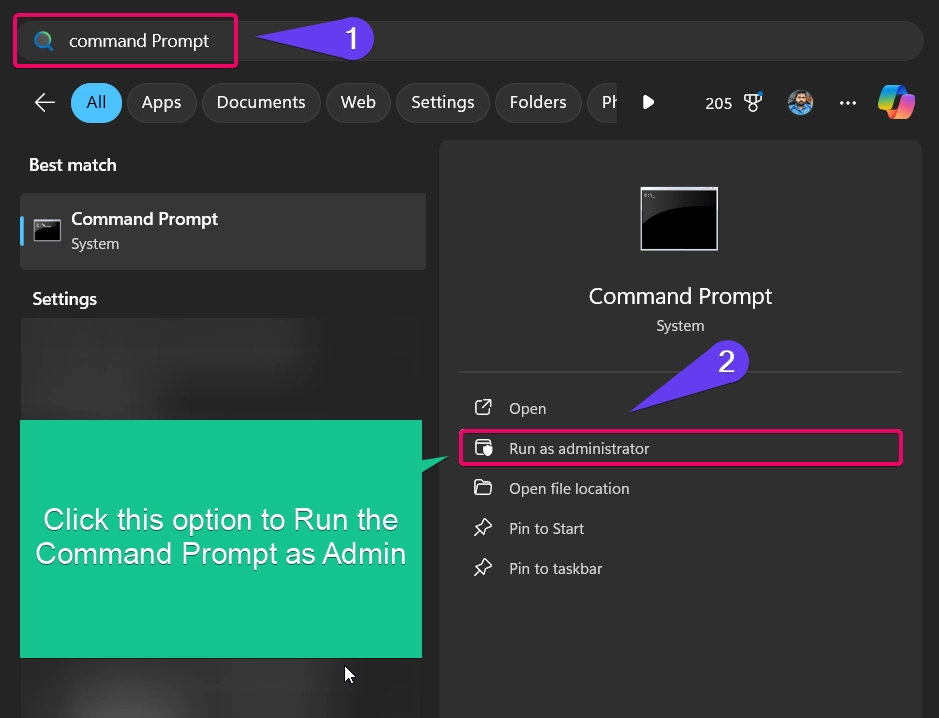
- In the search results, right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as Administrator.
- Alternatively, you can click Run as Administrator on the right-hand pane.
- If prompted, click Yes on the User Account Control (UAC) dialog box.
- Then the command prompt application will be launched with admin privileges.
Method 2: Run Command Prompt as Admin using Run Window:
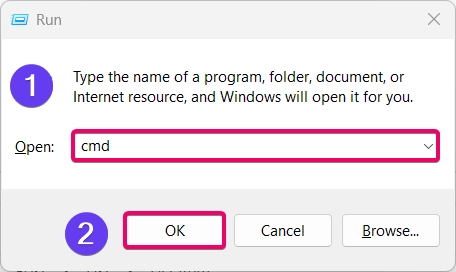
- Firstly, you need to launch the Run window using the keyboard shortcut.
- Winkey + R
- Then enter the keyword “cmd” and use the keyboard shortcut, CTRL + SHIFT + Enter.
- This key combination will launch the command prompt application with the admin privileges.

Method 3: Run Command Prompt as Admin using Search Shortcut:
- Firstly, you need to use the keyboard shortcut Winkey + S, It will launch the Windows Search Shortcut window.
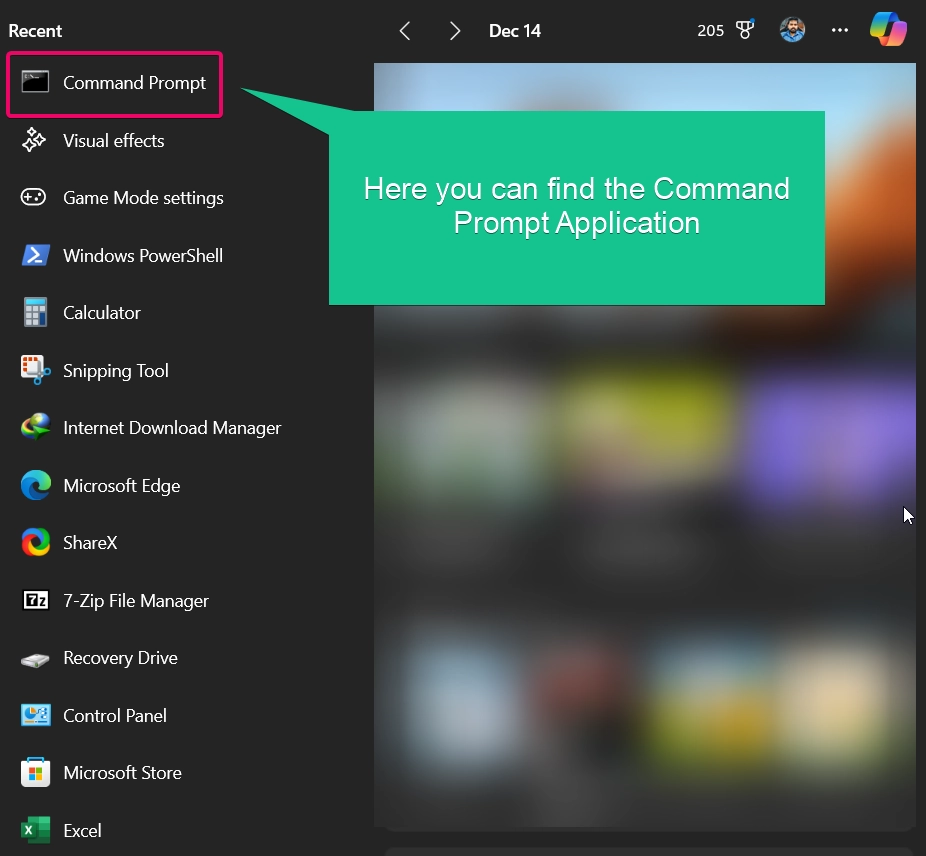
- Now, you need to right click on the command prompt and choose Run as Administrator option.
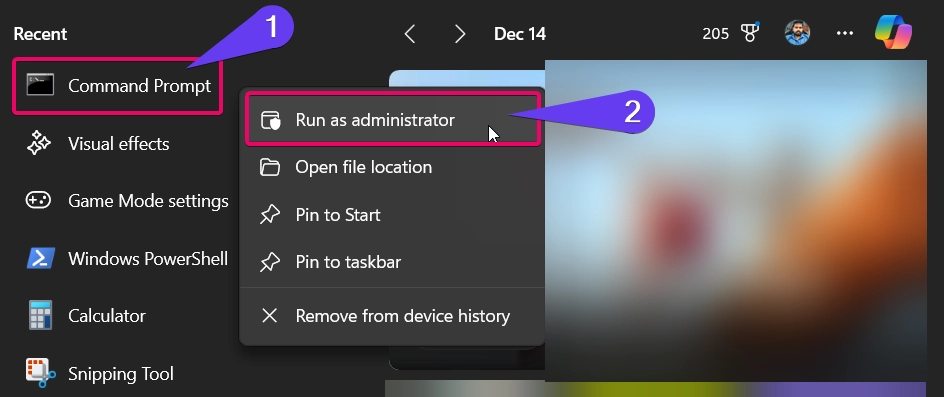
- After choosing the option, the command prompt application will be launched with admin privileges.

Method 4: Open Command Prompt as Admin using File Explorer:
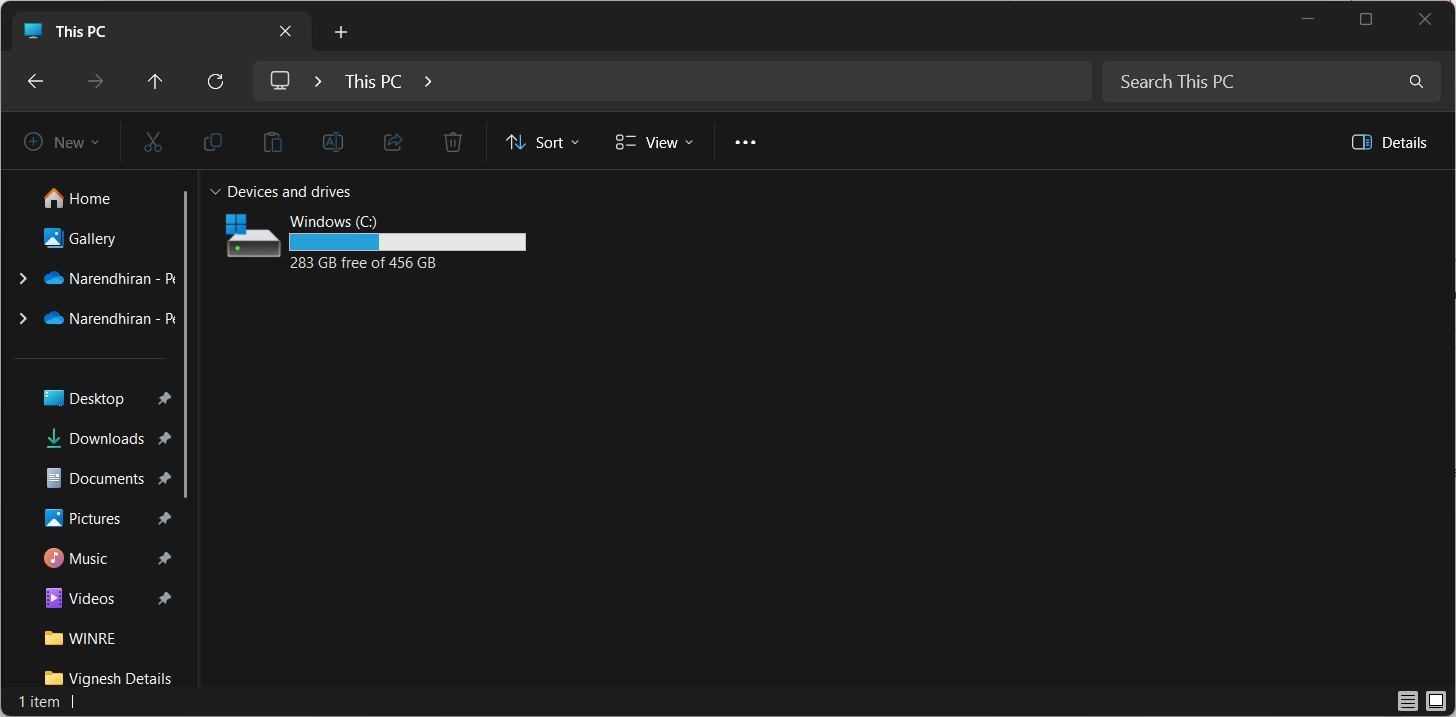
- Firstly, you need to open the File explorer using the keyboard shortcut: Winkey + E.
- Then, you need to go to This PC option.
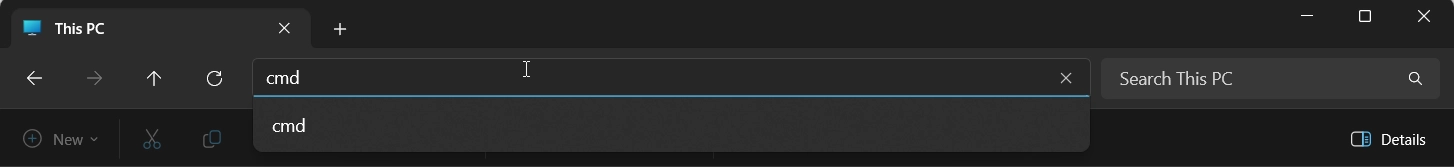
- Now, in the address bar, you need to run the command “cmd” and use the keyboard shortcut: CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER button.
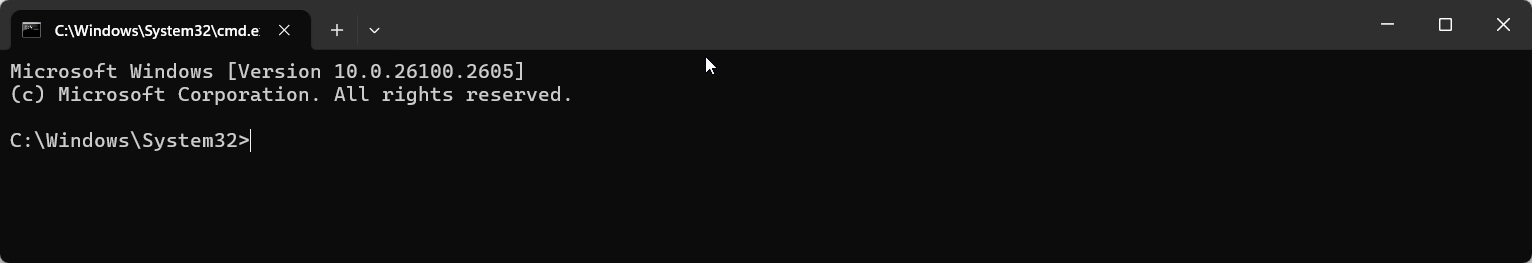
- This action will launch the command prompt application with admin rights.
Method 5: Using Task Manager:
- Use the keyboard shortcut: CTRL + SHIFT + Esc to launch the task manager on your pc.
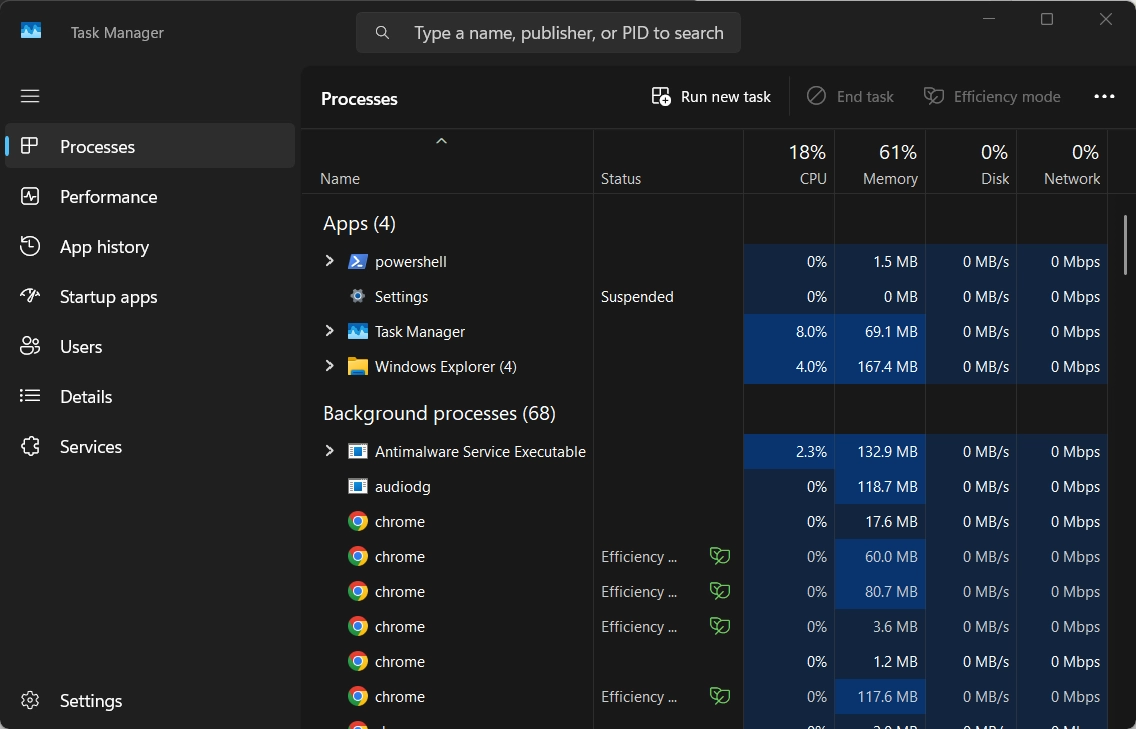
- In the right top, you can see the option named “Run New Task“.
- Click the option, it will launch a window which is similar to Run window.
- Then, you need to enter the command “cmd”
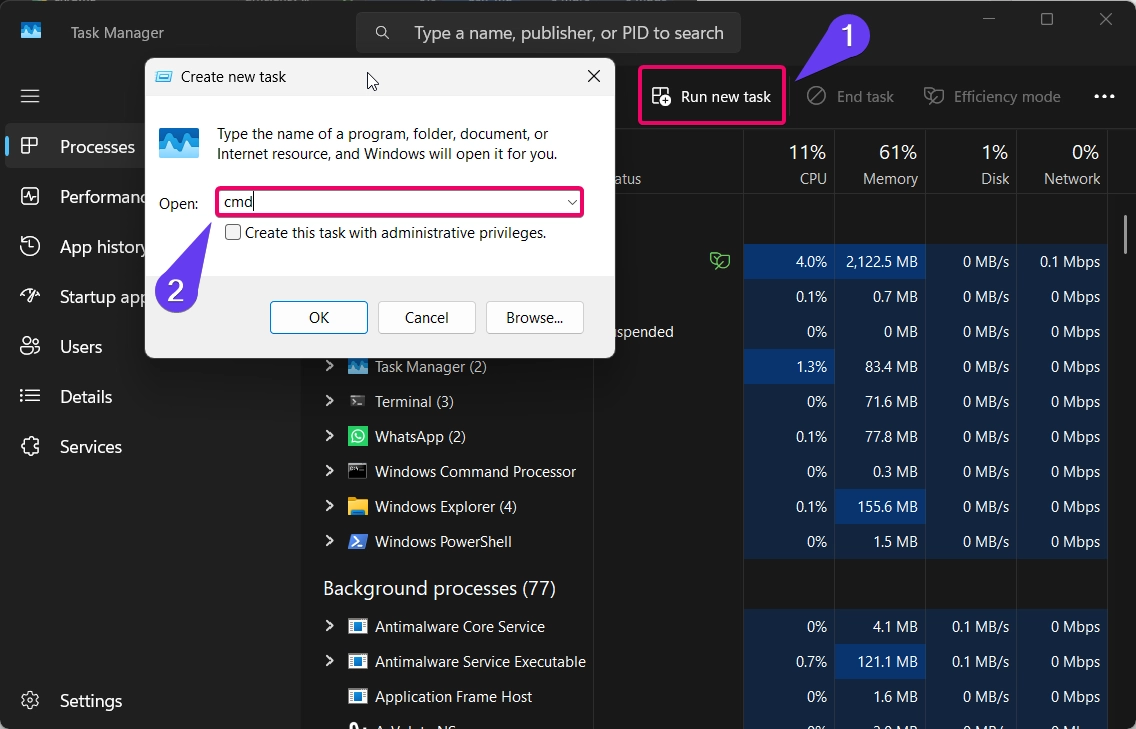
- Before clicking the ok button, don’t forgot to check the box named “Create this task with administrative privileges.“
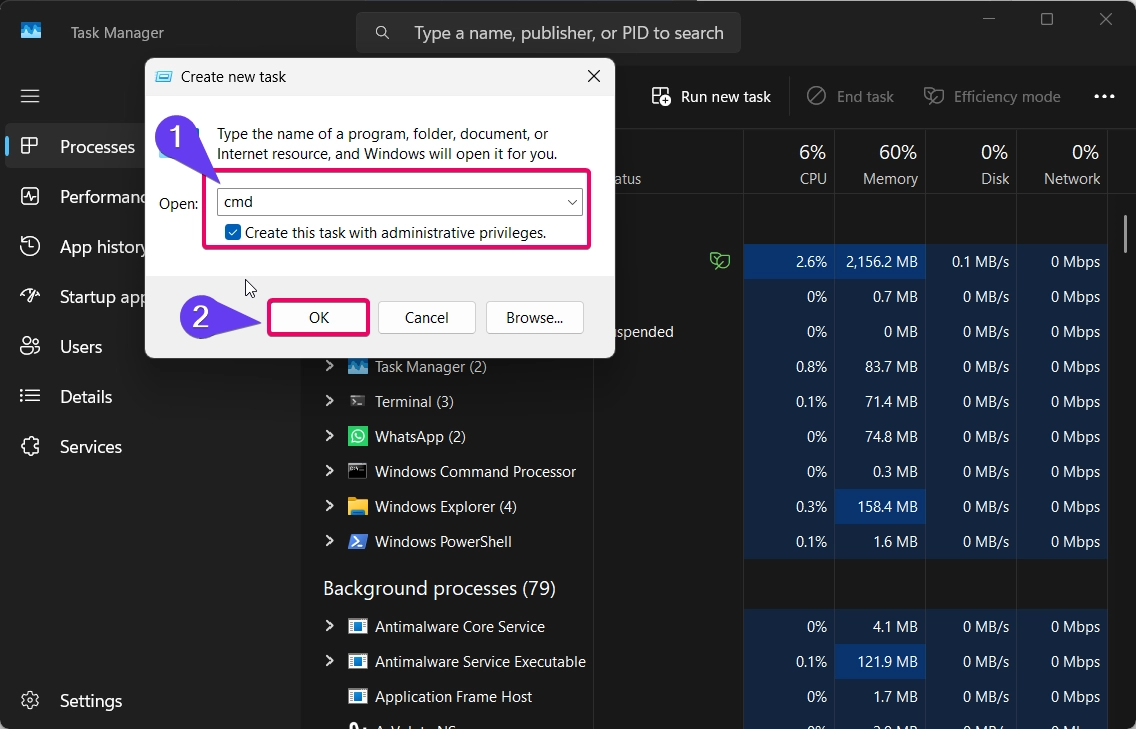
- Now, the command prompt app will launch with elevated admin rights.
Method 6: Using Windows Terminal:
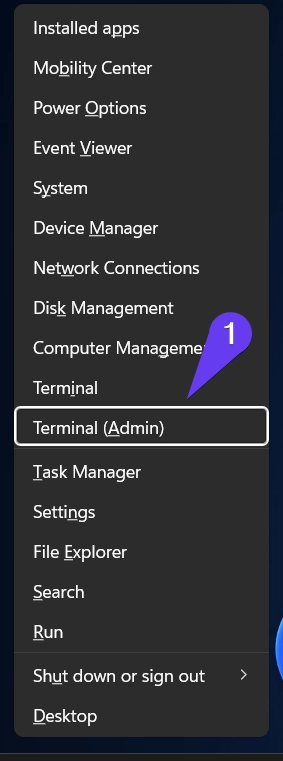
- Use the keyboard shortcut: Winkey + X to launch the Quick Access menu on your pc.
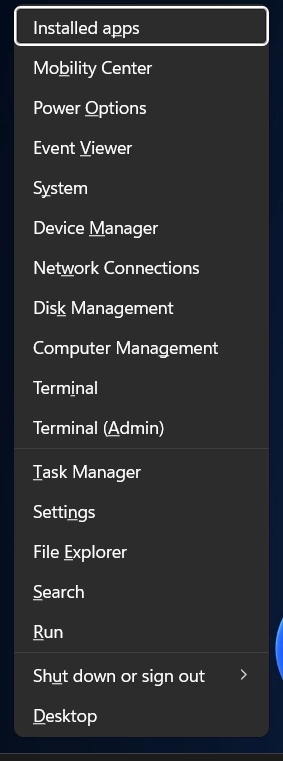
- Select Windows Terminal (Admin) from the list.
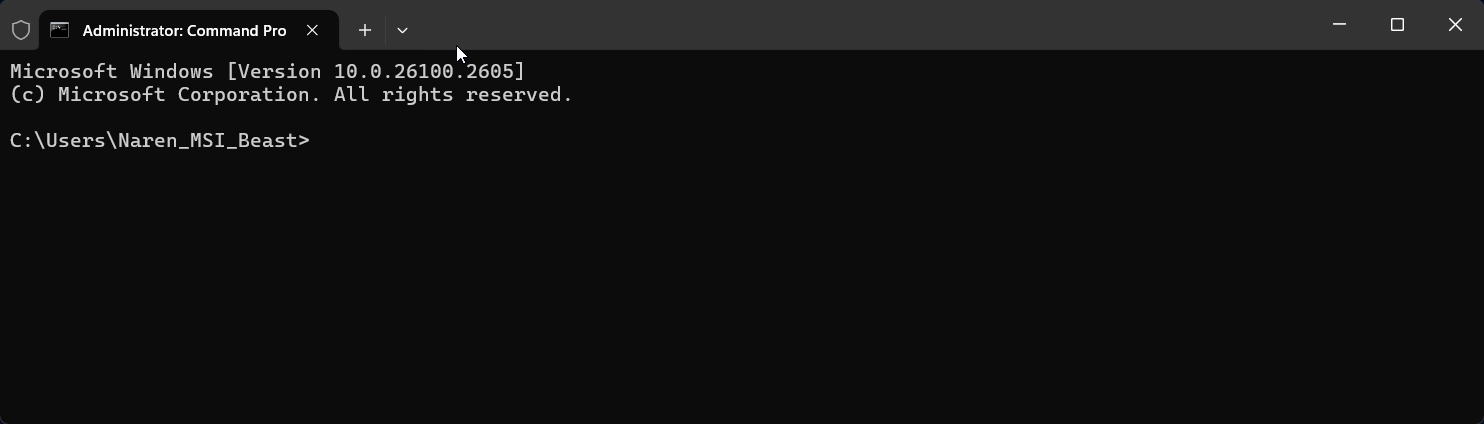
- If Windows Terminal opens to PowerShell or another shell, click the down arrow at the top of the Terminal window, select Command Prompt, and it will open with administrative privileges.
Method 7: Using Desktop Shortcut:
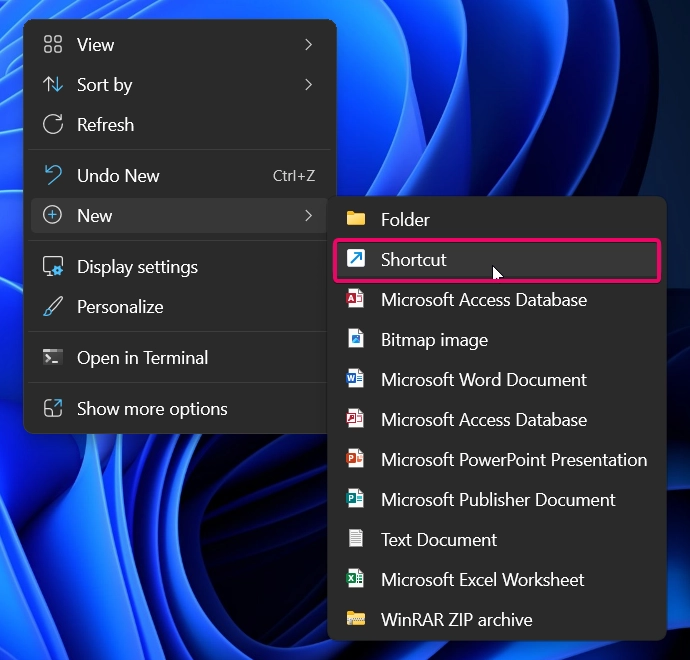
- Right-click on your desktop and select New > Shortcut.
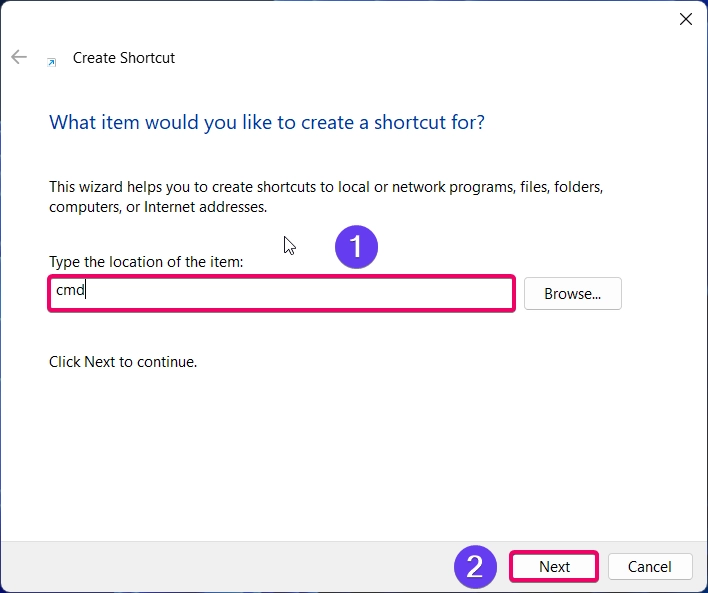
- Type
cmdas the location and click Next button.
- Name the shortcut (e.g., “Command Prompt Admin”) and click Finish.
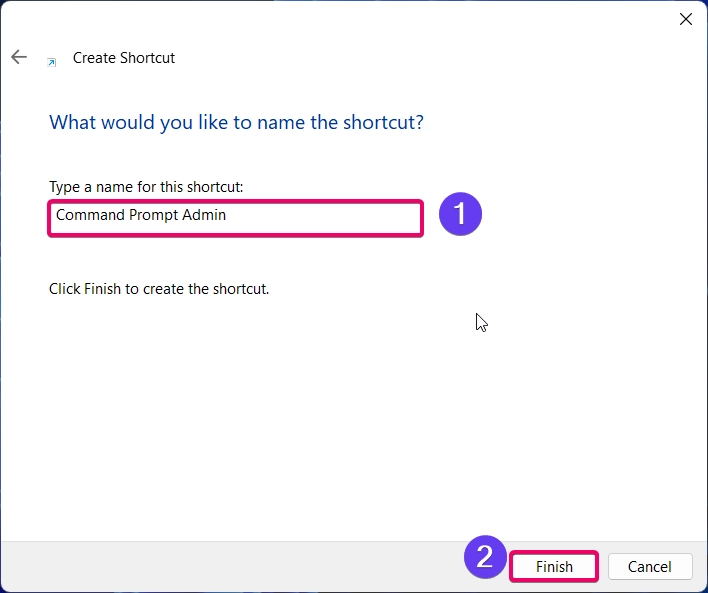
- Right-click on the created shortcut and choose Properties.
- Under the Shortcut tab, click on Advanced and check Run as administrator.
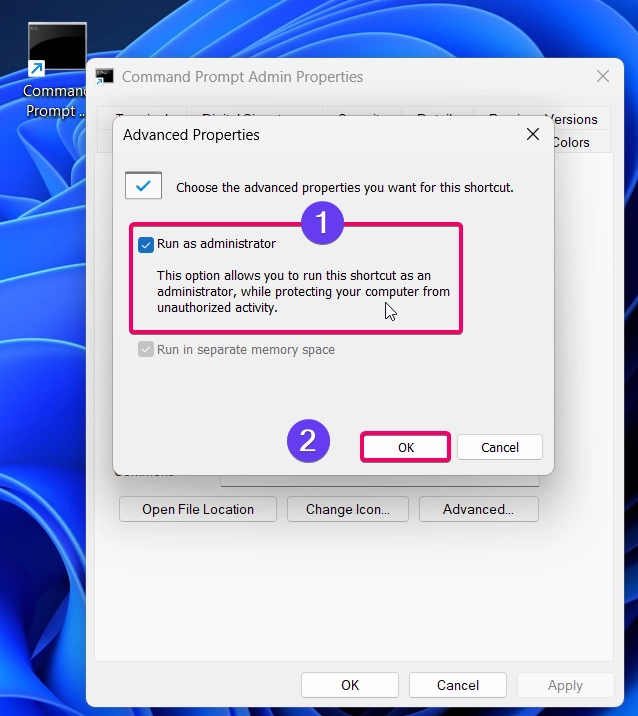
- Click OK, then Apply. Now, double clicking this shortcut will open Command Prompt as an administrator.

Conclusion
Running Command Prompt as an administrator is a crucial skill for performing advanced tasks in Windows 11. Using the methods listed above, you can easily elevate Command Prompt whenever needed. The above methods are tested and verified ones and the quickest one is Method 1, 2 & 7. The shortcut method is permanent one, once you have created it will launch the command prompt with elevated admin rights whenever it is accessed. Find more interesting tutorials on Winsides.com
 How to use Microsoft iSCSI Initiator on Windows 11?
How to use Microsoft iSCSI Initiator on Windows 11? How to Enable Game Mode on Windows 11?
How to Enable Game Mode on Windows 11? How to Check PC Specs without Logging into Windows 11?
How to Check PC Specs without Logging into Windows 11? How to Enable HDR Video Streaming on Windows 11?
How to Enable HDR Video Streaming on Windows 11?