Windows Process Activation Service, also known as WAS, is a Windows operating system component that provides process model and activation services for applications that use Internet Information Services (IIS). It’s particularly important for hosting applications that require a process model beyond what the traditional IIS worker process (w3wp.exe) provides. WAS plays a crucial role in managing and activating processes related to web applications, services, and other network-related functionalities. It helps in managing application pools, process recycling, and ensuring that applications run smoothly within the IIS environment. In this article, we will check out the steps involved in the process of enabling Windows Process Activation Service in Windows 11.
- Click on the Start Menu and open the Control Panel.
- Switch the Control Panel view to Category.

Category View - Now, Click on Programs.

Programs - Under Programs and Features, click on Turn Windows Features on or off.
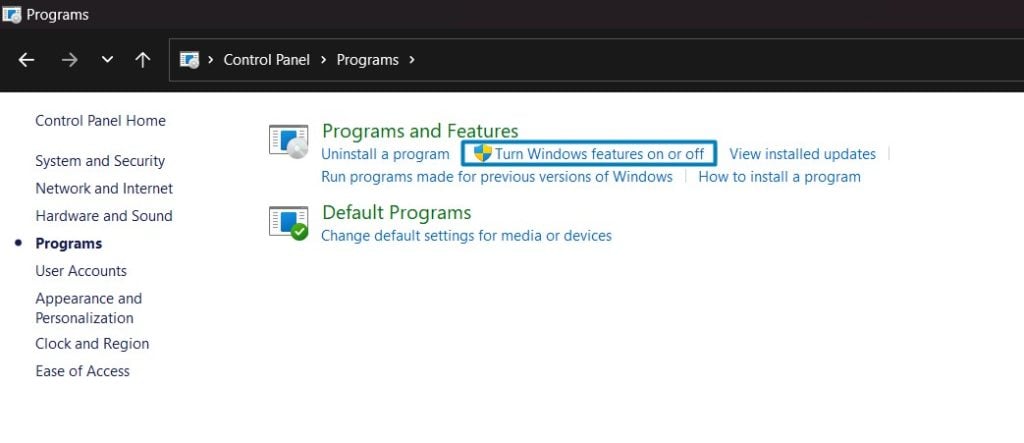
Turn Windows Features on or off - Windows Features dialog box will open now.
- Search and locate Windows Process Activation Service from the list of services available.
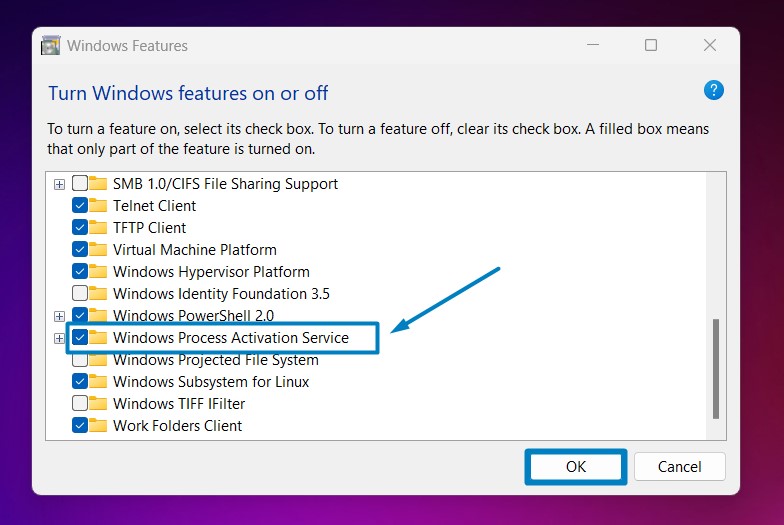
Enable Windows Process Activation Service in Windows 11 - Click on the checkbox next to it and then click on OK.
- Windows 11 will search for the required files.
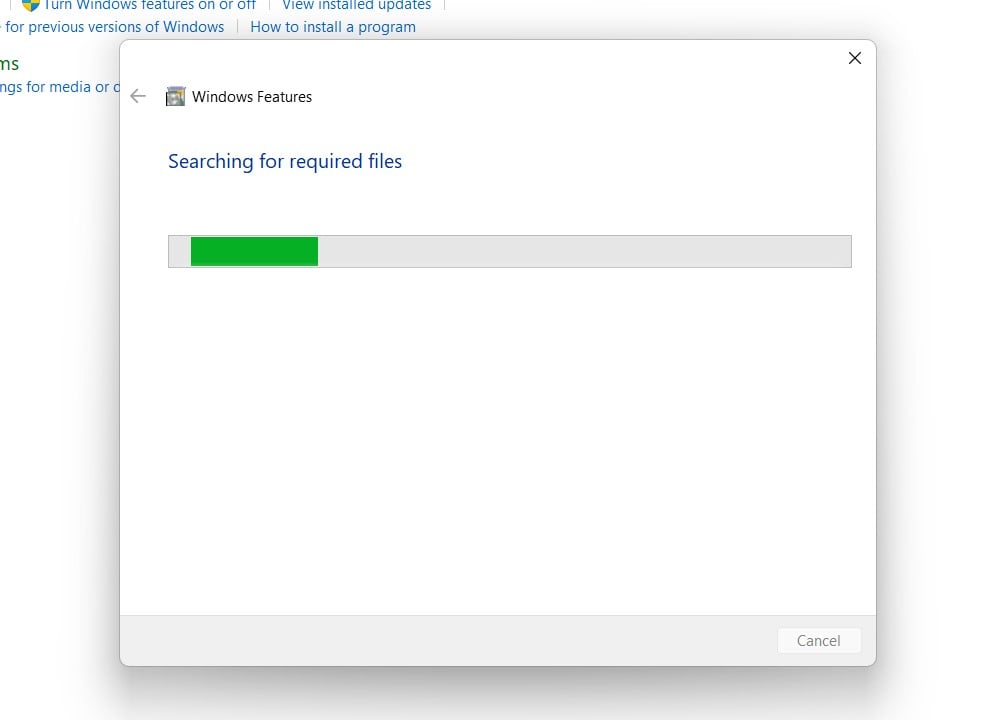
Searching for the required files - After the process, Windows will apply the necessary changes.
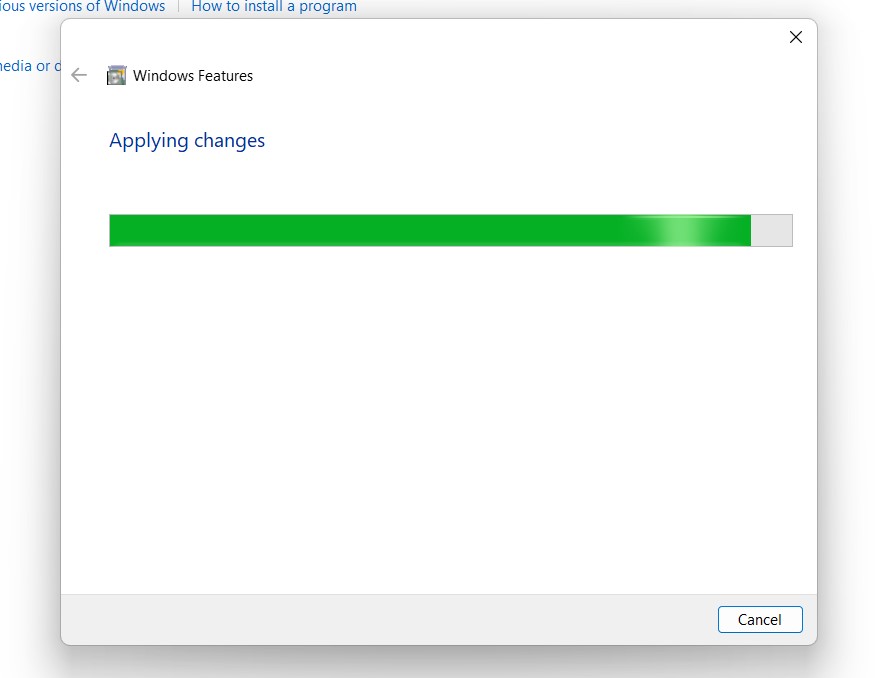
Applying Changes - The system will prompt for a restart. Click Close. Continue with Restart if prompted. It is recommended that changes made to the system reflect while using the environment.
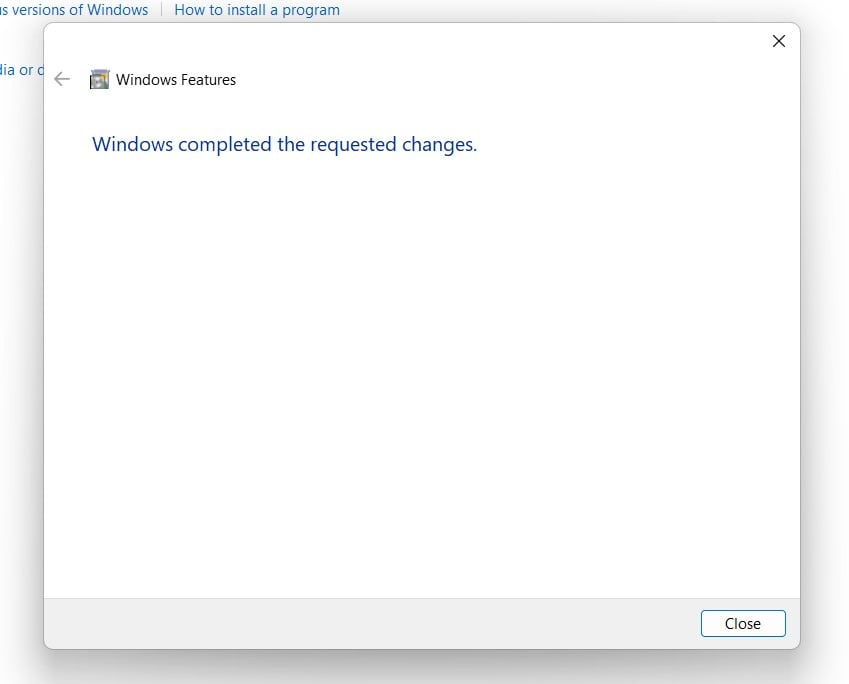
Close - Windows Process Activation Service is now enabled on your Windows 11 laptop or PC. Enjoy Seamless Connectivity.
Key Features of Windows Process Activation Service [WAS]:
WAS supports various protocols and services, including HTTP, HTTPS, TCP, and Named Pipes, making it versatile for web and network applications. It’s a fundamental part of the infrastructure for hosting web services and applications on Windows servers. The following are some of the key features of WAS.
- Process Activation: As the name suggests, WAS is responsible for activating and managing worker processes for web applications hosted on Internet Information Services (IIS). It ensures that applications are launched and run efficiently in response to incoming requests.
- Application Pool Management: It provides robust management capabilities for application pools. Application pools help isolate web applications, providing reliability and security by ensuring that one application’s issues do not affect others.
- Protocol Support: WAS supports a range of protocols including HTTP, HTTPS, TCP, and Named Pipes. This flexibility allows the hosting of various types of web applications and services, catering to different communication requirements.
- Integration with IIS: WAS tightly integrates with Internet Information Services (IIS), enhancing IIS’s capabilities by providing advanced process management and activation services.
- Configuration Flexibility: Admins can configure WAS settings through the IIS Manager or programmatically using PowerShell or the .NET Framework. This flexibility enables fine-tuning process activation and management according to specific requirements.
- Automatic Process Recycling: WAS can automatically recycle worker processes based on configurable settings such as memory usage, CPU utilization, or time elapsed. This helps maintain application stability and performance over time.
Worker processes are the active components responsible for handling incoming requests, executing application logic, and generating responses in web hosting environments. They play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation and performance of web applications and services on servers.
Take away:
Windows Process Activation Service (WAS) in Windows 11 is a vital component for hosting web applications and services. WAS’s ability to manage worker processes, isolate applications, handle high traffic loads, and maintain server stability contributes significantly to the smooth operation and performance of web hosting environments. Happy Coding! Peace out!
![How to Enable IIS [Internet Information Services] in Windows 11? 1 Enable IIS in Windows 11](https://winsides.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/IIS-in-Windows-11-390x220.webp) How to Enable IIS [Internet Information Services] in Windows 11?
How to Enable IIS [Internet Information Services] in Windows 11? How to Enable Simple TCP/IP Services in Windows 11?
How to Enable Simple TCP/IP Services in Windows 11? Enable SMB 1.0 / CIFS File Sharing Support using Command Prompt & Windows PowerShell
Enable SMB 1.0 / CIFS File Sharing Support using Command Prompt & Windows PowerShell Enable SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support in Windows 11
Enable SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support in Windows 11