How to Run Regedit as Administrator on Windows 11?- 5 Best Ways!
Windows Registry Editor is a Hierarchical Database that Stores Low-Level Settings & Configurations
Registry Editor is the backend side of the essential windows files. Regedit, is a powerful tool that allows users to view, edit, and manage the Windows registry. The registry serves as a database that stores low-level settings for the operating system and installed applications. While you can access the Registry Editor with standard permissions, certain changes and configurations require administrative privileges to execute successfully. To modify, create or edit the registry files you should definitely need elevated admin rights and so in this tutorial, I’ve added the detailed information about Run Regedit as Administrator on Windows pc.
Multiple Ways to Run Regedit as Administrator on Windows 11 OS
From the Start menu, to creating a dedicated Shortcut for Windows Registry Editor, there are several ways with which you can access this app with administrative privileges on Windows 11.
- Use the Start menu, and open Windows Registry Editor as Administrator.
- Open Regedit as Administrator using the Run Command.
- Create Task to Launch Regedit as Administrator using the Task Manager.
- Always open Regedit with Administrative Privileges by creating a Dedicated Shortcut.
- Launch Command Prompt with Elevated Permissions and then open Windows Registry Editor.
IMPORTANT: Running applications as an administrator grants elevated privileges that can significantly affect your system. Please use caution when doing so, as it can lead to Unintended System Modifications, Security Vulnerabilities, Accidental Data Loss, Unauthorized Access, Irreversible Changes, etc.
1. How to open Regedit as Administrator using the Start menu?
This is the easiest method to open this App on Windows 11 with Elevated privileges.
- Go to the Start menu. You can also use the key combination WinKey + S.
- In the Search bar, search for regedit.
- The system will display the Registry Editor Application. Right-click on it and then click on Run as Administrator.
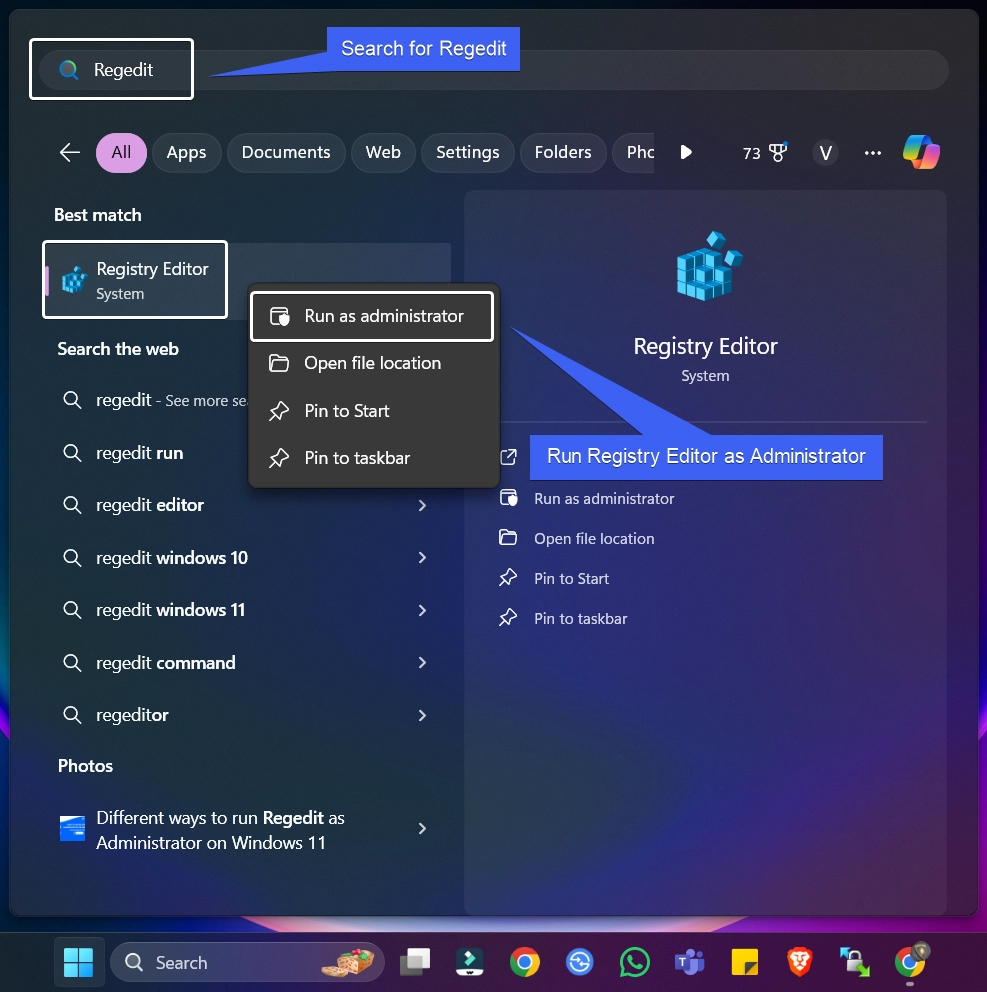
- The User Account Control will prompt user’s confirmation and open Regedit with Administrative Privileges on Windows 11.
IMPORTANT: Running applications as an administrator grants elevated privileges that can significantly affect your system. Please use caution when doing so, as it can lead to Unintended System Modifications, Security Vulnerabilities, Accidental Data Loss, Unauthorized Access, Irreversible Changes, etc.
2. Use the Run Command and open Regedit as Admin on Windows 11
This method is very handy especially if you are used to “Run Command”.
- Go to the Run Command using the shortcut WinKey + R.
- In the Run, type the following command
regeditand press CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER.
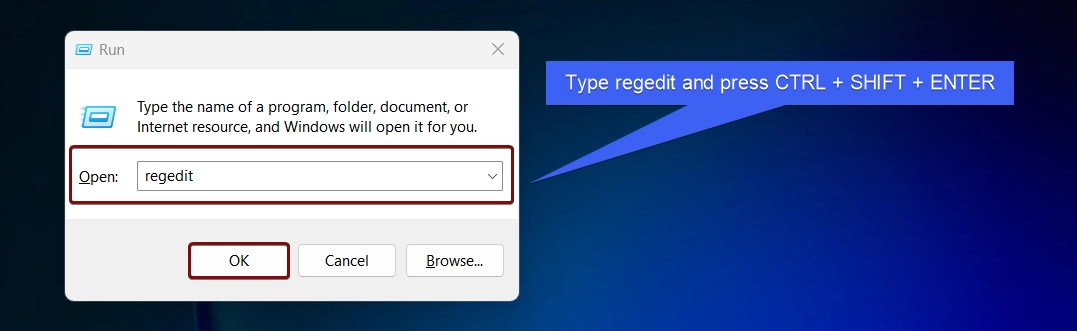
- This will inform the system to run this command with administrative privileges.
- The System will prompt your confirmation and then open Windows Registry Editor with Administrative Privileges.
3. Create New Task to Launch Windows Registry Editor with Administrative Privileges using the Task Manager
It is very easy to create New Tasks using Task Manager. Here in this section, we will checkout how to run Regdit as Admin using the Task Manager.
- Right-click on the Taskbar and click Task Manager. You can also use the shortcut CTRL + SHIFT + ESC. This combination will open Task Manager directly.
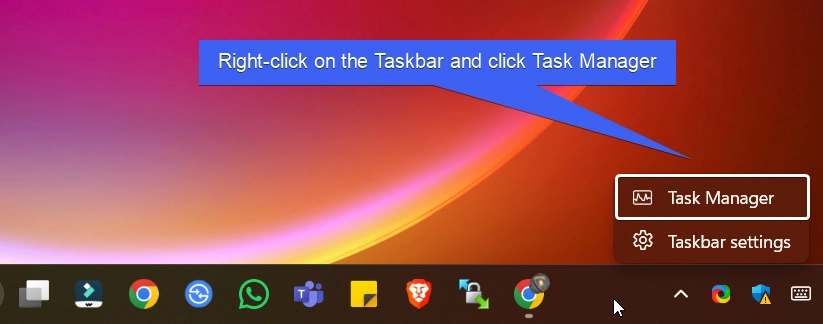
- In the Task Manager, under Processes, click on Run New Task. Create New Task dialog will pop up now.
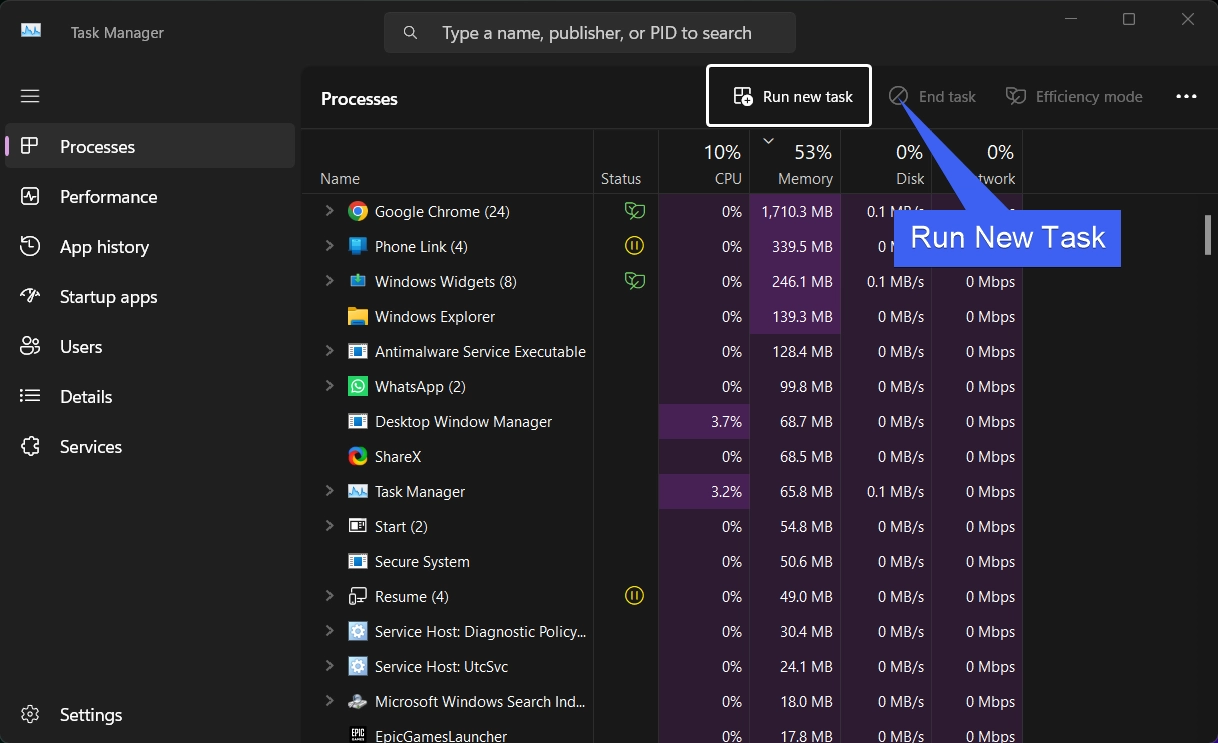
- Type the command
regeditand enable the checkbox “Create this Task with Administrative Privileges“. Finally, click OK.
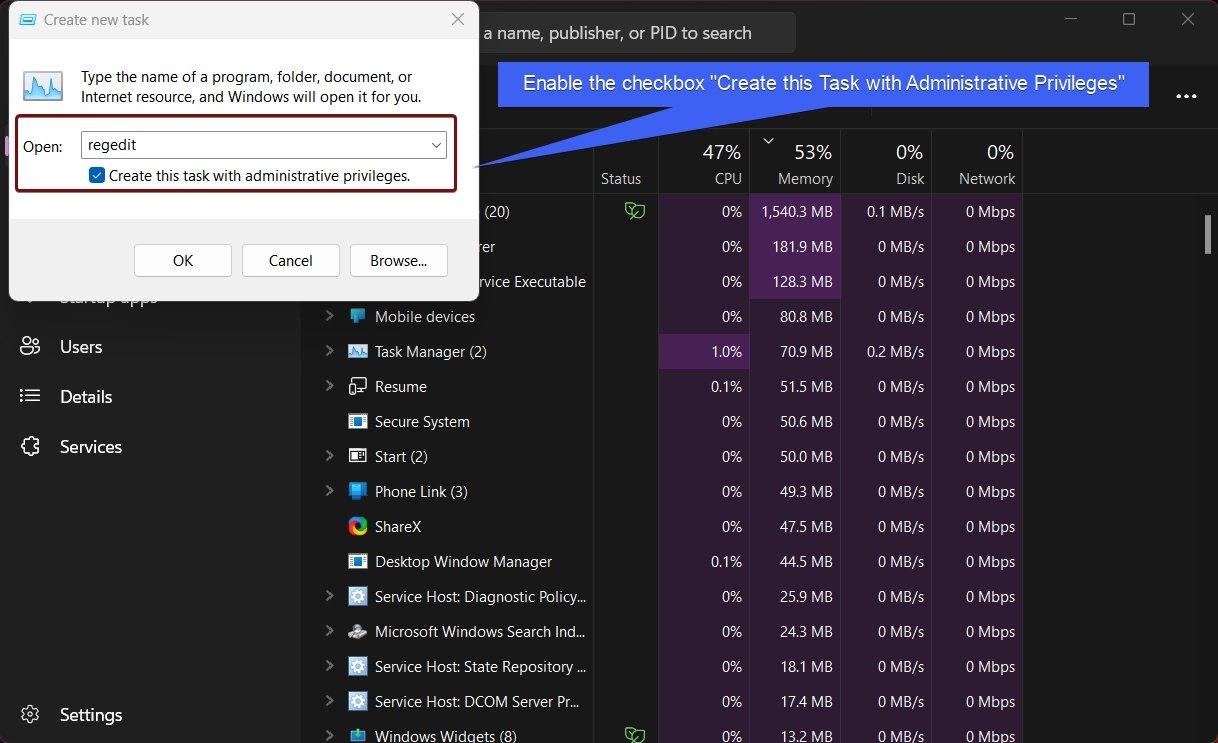
- The system will open Windows Registry Editor with Administrative Privileges.
4. Always open Regedit with Administrative Privileges by creating a Desktop Shortcut
This method is useful for users who frequently uses Registry Editor with Elevated Permissions. We can create a dedicated Regedit Desktop Shortcut with Administrative Privileges.
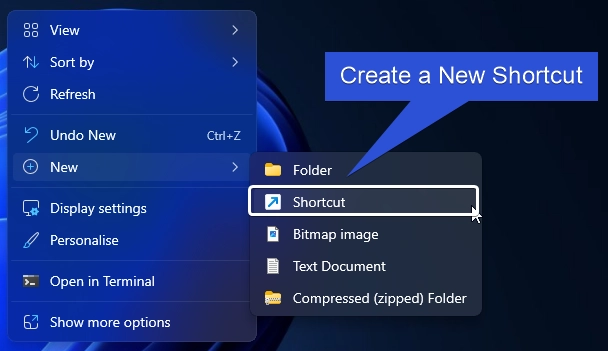
- Right-click on the Empty space of the Desktop, and click New > Shortcut.
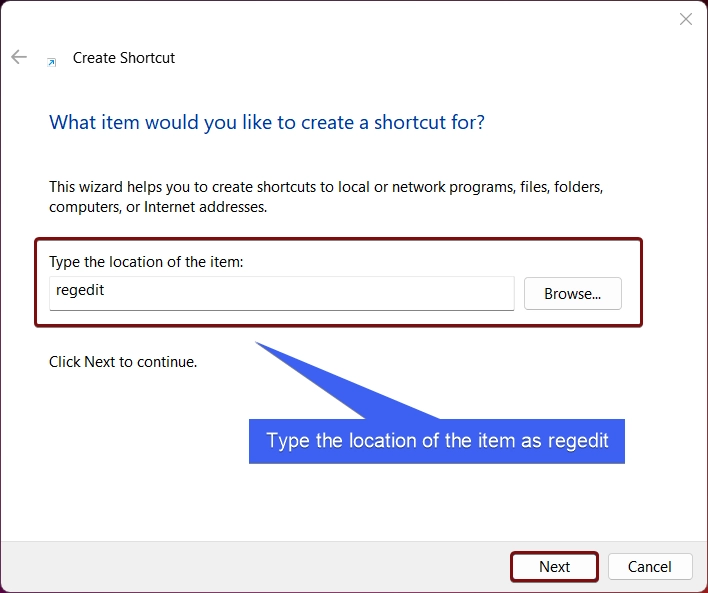
- The Create Shortcut dialog box will open now. In “Type the Location of the Item“, enter the command
regedit. Click Next. If you face any issues, then you can enter the full pathC:\Windows\regedit.exe
- The system will assign the shortcut name regedit. You can change it to Windows Registry Editor if you want to. Finally, click Finish.
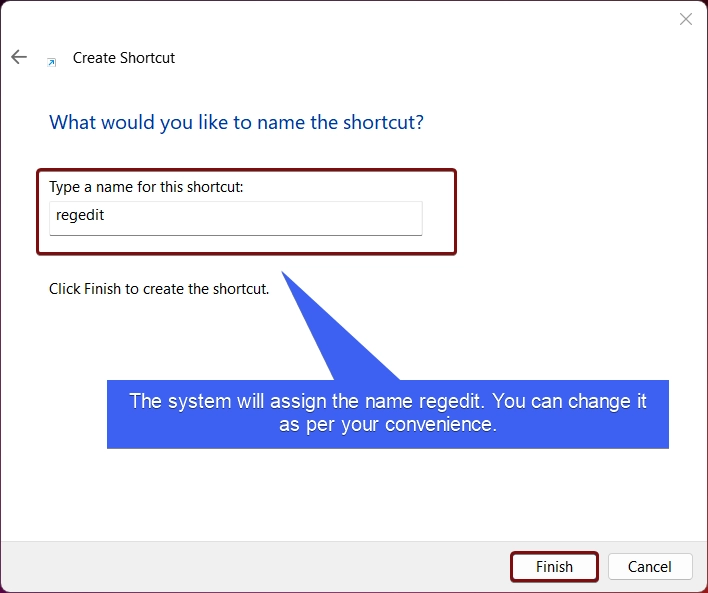
- Windows Registry Editor Desktop Shortcut will be created.

- Right-click on the Shortcut and click on Properties.
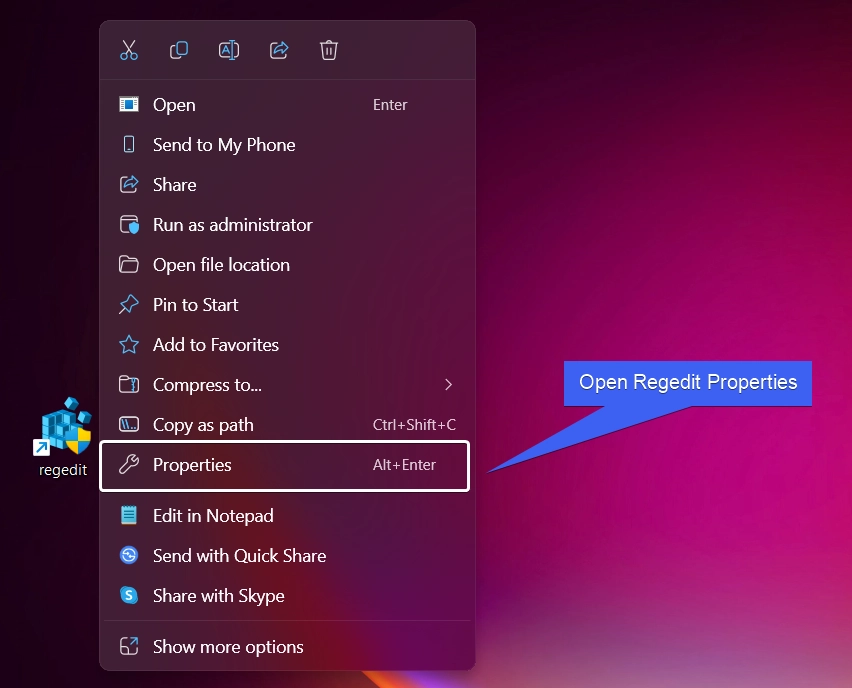
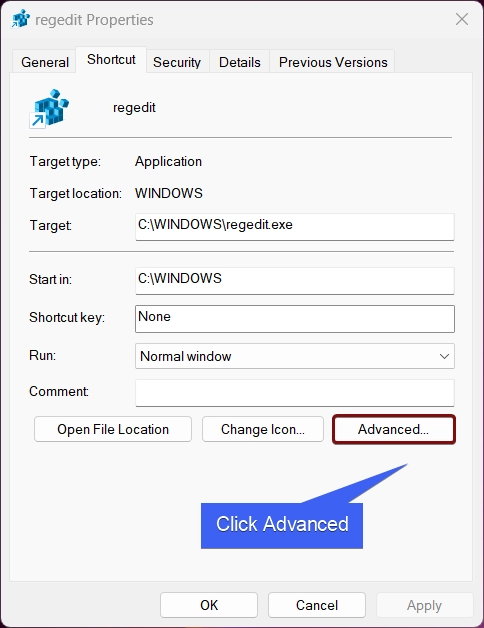
- Regedit Properties will open now. Click Advanced.
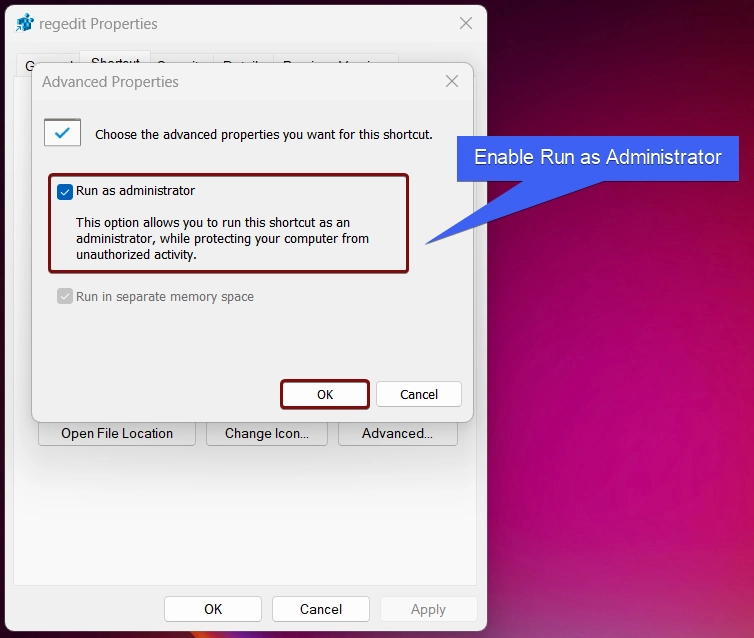
- In Advanced Properties, make sure to enable the checkbox “Run as Administrator“. This option allows you to run this shortcut as an administrator, while protecting your computer from unathorized activity. Finally, click OK, and then Apply.
5. Launch Command Prompt with Elevated Privileges and open Regedit
This method is useful for users who use Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell frequently. You can either use any of these, in this article, for explanation, I am using Command Prompt.
- Open Command Prompt via the Start menu, right-click on it and Run as Administrator.
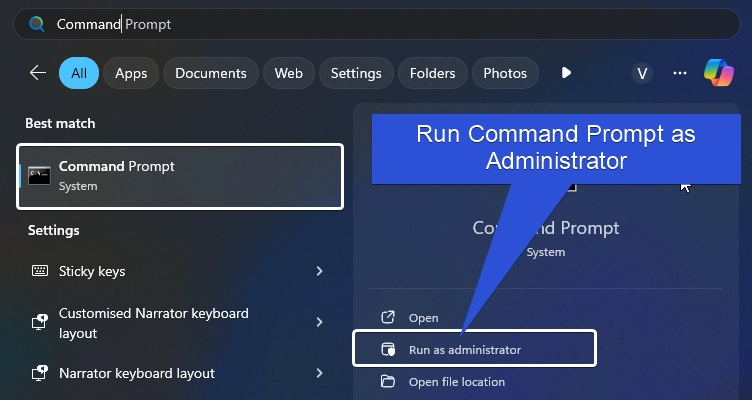
- UAC will confirm and open CMD with Administrative Privileges.
- In the Command Prompt, type the command
regeditand press Enter.
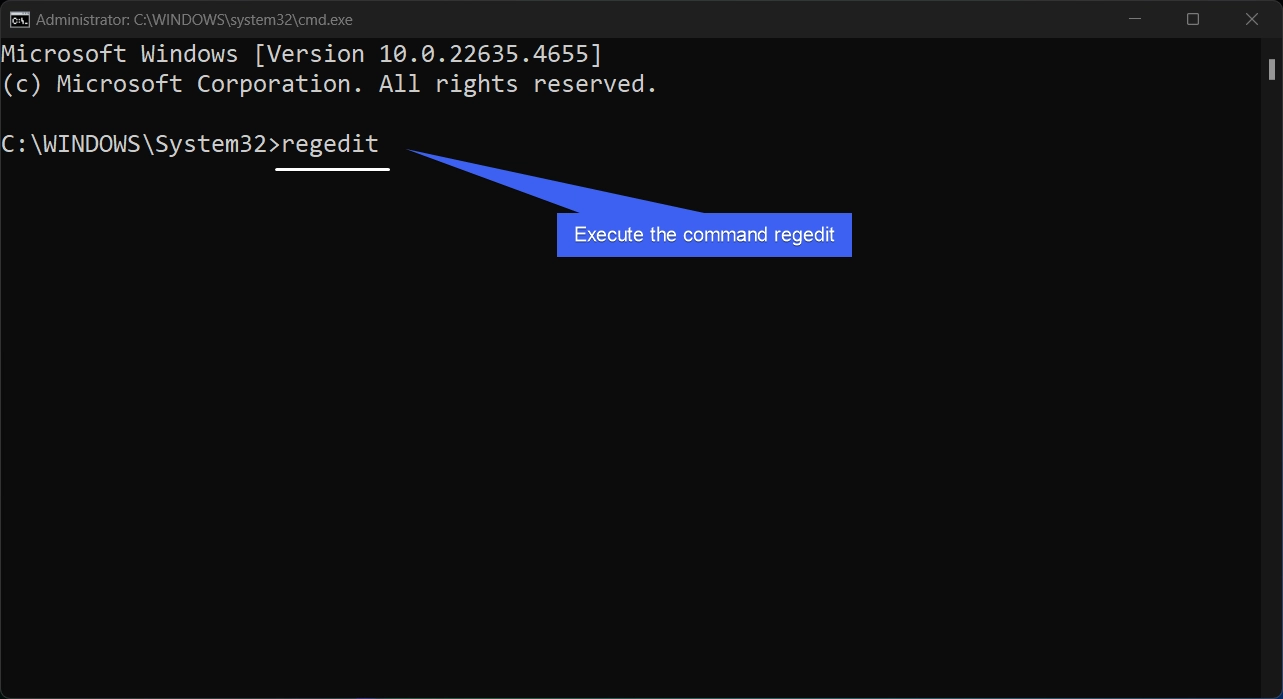
- The system will open Windows Registry Editor with Elevated Permissions.
Kindly be Cautious while running an App as Administrator

Running Windows Registry Editor as Administrator on Windows 11 grants it elevated privileges, which can potentially bypass system security restrictions. Please proceed with care and only run trusted applications in this mode. At Winsides.com, we advise our users to use Administrator privileges only when absolutely necessary to perform tasks requiring elevated rights. Misuse of administrative privileges may lead to System Vulnerabilities, Data Loss, System Instability, Security Concerns, Irreversible Changes, etc.
Take away:
Whether you’re troubleshooting issues, modifying system settings, or enabling hidden features regedit is the only way to do this! By running Regedit as an administrator, you gain the required permissions to make impactful system level changes. I will recommend you to take backup of your registry files before modifying or creating registry files. If you have any queries related to the above topic and then kindly comment us below. Find more interesting tutorials on Winsides.com.
We combine expert insights with user-friendly guidance. We thoroughly research and test everything to give you reliable and simple to understand tech guides. Please take a look at our publishing process to understand why you can trust Winsides.



